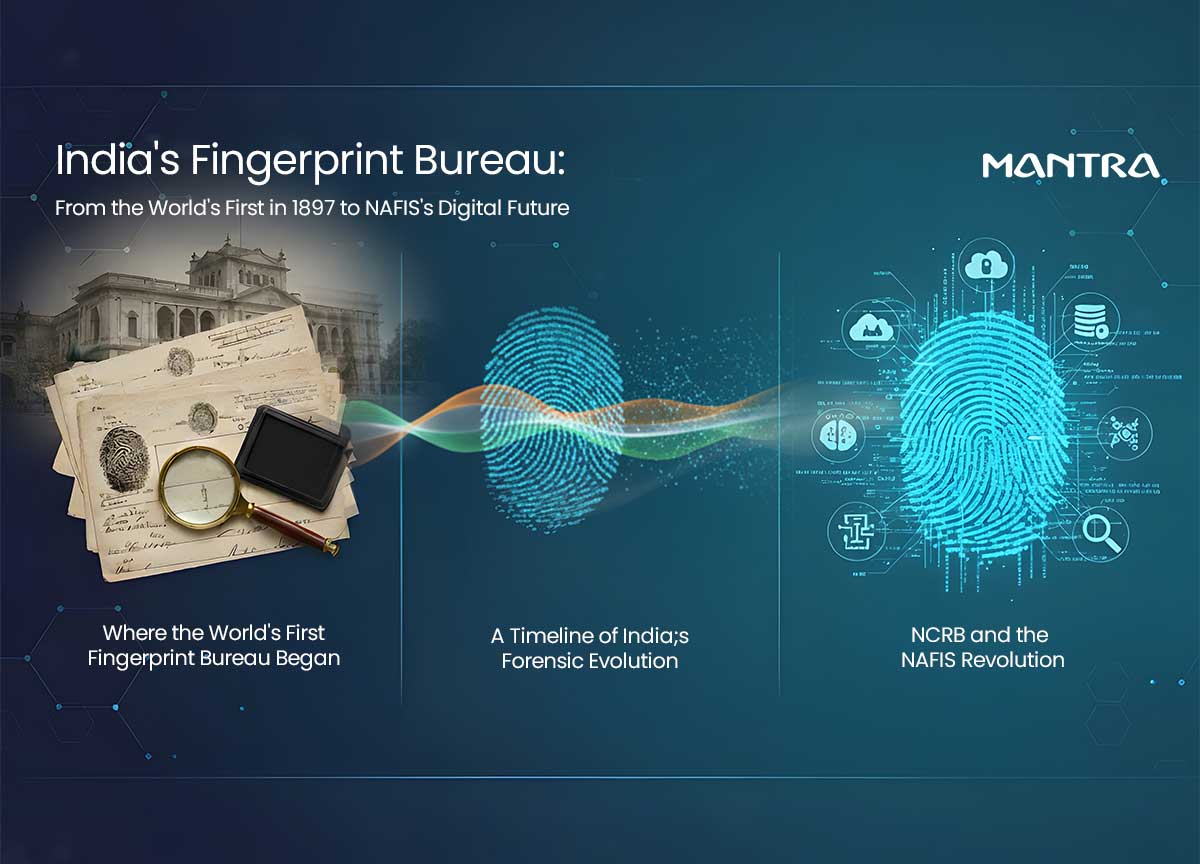
Introduction
India's Fingerprint Bureau is undergoing a monumental transformation, blending a rich, pioneering history with cutting-edge technology to redefine forensic science and national security. At the heart of this evolution is the Indian government's strategic push to create a unified, digital-first forensic ecosystem. This initiative, driven by the Ministry of Home Affairs, is revolutionizing how crime is solved across the nation.
This article provides a comprehensive, news-focused look at the journey of the Fingerprint Bureau. We'll explore its historic origins as the world's very first bureau, unpack the game-changing National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS), and provide a clear, easy-to-use directory of key Fingerprint Bureau offices across India.
Key Facts
To provide the clearest information, here are the essential facts about India's Fingerprint Bureau and its modernization:
The world's first-ever Fingerprint Bureau was established in Kolkata (then Calcutta), India, in 1897.
India launched its National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS) on August 17, 2022, to create a central database of criminal fingerprints.
NAFIS assigns a unique 10-digit National Fingerprint Number (NFN) to every arrested individual for lifelong tracking.
The Central Fingerprint Bureau (CFPB) operates under the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) in New Delhi and is the central authority for fingerprint data in India.
As of late 2024, the NAFIS repository contains over 1.06 crore criminal fingerprint records accessible to law enforcement agencies nationwide.
Where the World's First Fingerprint Bureau Began
The story of modern forensics has its undisputed origin in India. Long before Scotland Yard or the FBI adopted fingerprinting, the science was perfected in Bengal.
The Kolkata Fingerprint Bureau, established in 1897, holds the unique distinction of being the world's first. Under the administration of Sir Edward Richard Henry, two Indian sub-inspectors, Azizul Haque and Hemchandra Bose, developed a groundbreaking classification system. This "Henry Classification System" was the breakthrough that allowed fingerprints to be organized and searched practically on a large scale. Its success was so profound that it was adopted by Scotland Yard in 1901 and became the global standard for the next century.
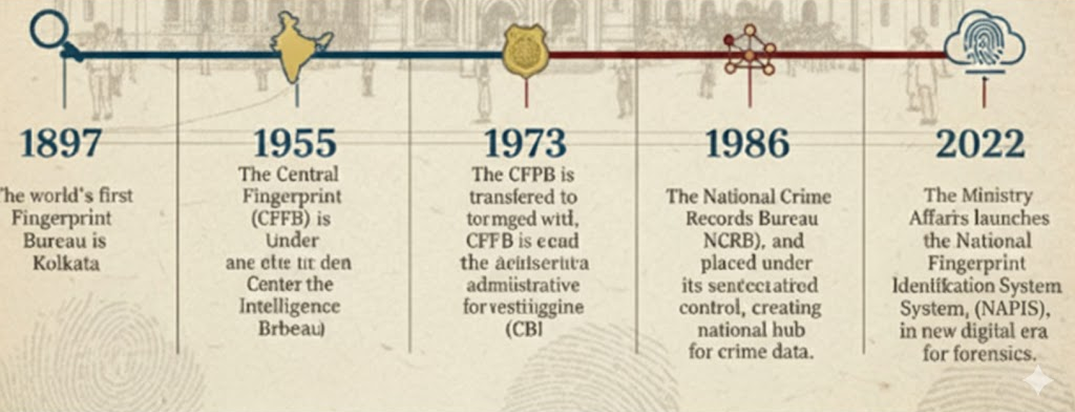
Timeline of India’s Resurgence in Biometrics
A Timeline of India's Forensic Evolution
For most citizens, interaction with a Fingerprint Bureau is for international verification and background checks. These bureaus are the only authorized government bodies for these services.
1897: The world's first Fingerprint Bureau is established in Kolkata.
1955: The Central Fingerprint Bureau (CFPB) is established under the Intelligence Bureau.
1973: The CFPB is transferred to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
1986: The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) is formed, and the CFPB is placed under its administrative control, creating a national hub for crime data.
2022: The Ministry of Home Affairs launches the National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS), ushering in a new digital era for forensics.
NCRB and the NAFIS Revolution
While history provides the foundation, the current news is the government's aggressive push towards a centralized, technology-driven forensic framework.
What is the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)?
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), established in 1986, is an Indian government agency under the Ministry of Home Affairs. Its primary function is to collect and analyze crime data. It serves as the central repository for criminal information, empowering investigators to link crimes to perpetrators across state lines. The NCRB is the parent body that manages both the Central Fingerprint Bureau and the NAFIS project.
What is NAFIS?
The National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS) is the cornerstone of India's forensic modernization. Launched in August 2022, NAFIS is a pan-India, searchable database of criminal fingerprints. Managed by the NCRB, it provides a 24/7, real-time digital platform for law enforcement agencies to upload, trace, and retrieve fingerprint data from anywhere in the country.
How NAFIS Works:
Centralized Database -
It connects the fingerprint databases of all States, Union Territories, and central agencies into one unified system.
National Fingerprint Number (NFN) -
Every arrested person is assigned a unique 10-digit NFN. This ID is used for their entire lifetime, linking all crimes and FIRs to a single, unique record.
Real-Time Identification -
The system allows for rapid identification of suspects by matching prints from a crime scene against the national database. Madhya Pradesh became the first state to successfully use NAFIS to identify a deceased person in April 2022.
Major Fingerprint Bureau Offices in India
While every state has a Fingerprint Bureau (typically at the State Crime Records Bureau or CID headquarters), certain centers are strategically important. Below is a structured list of key bureau offices.
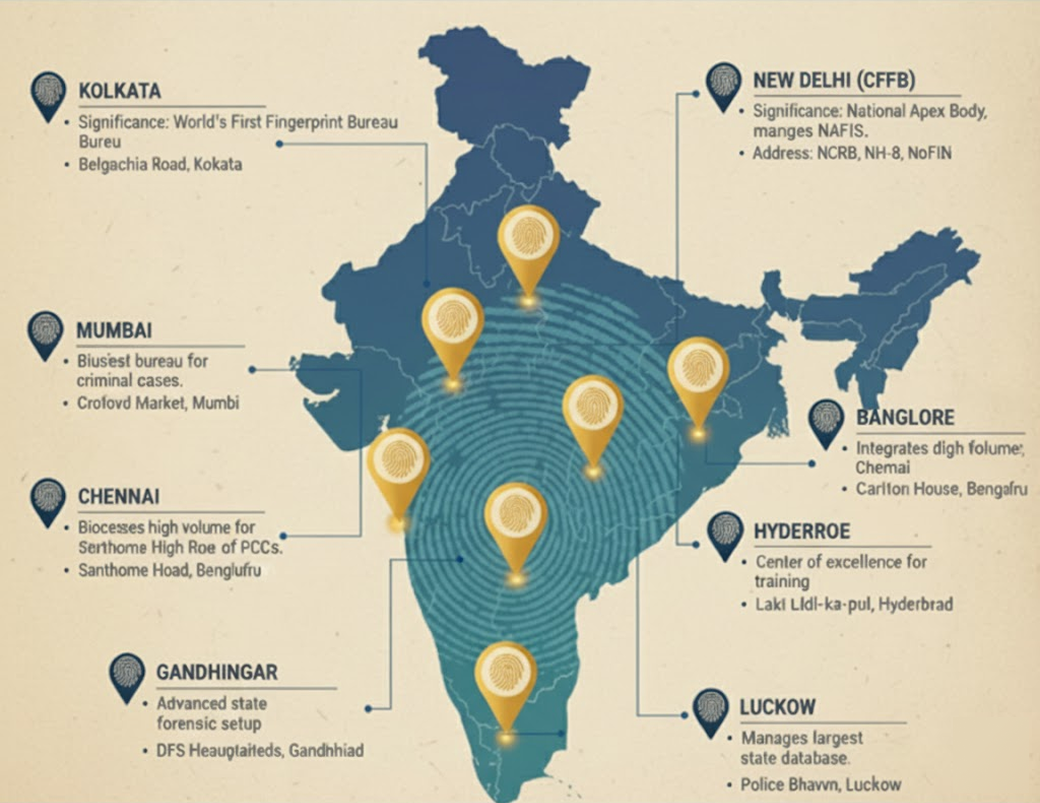
8 Fingerprint Bureau Offices with their Addresses
| Bureau / City | Significance | Full Address |
|---|---|---|
| Kolkata | World's First Fingerprint Bureau, historic birthplace of modern fingerprinting. | Finger Print Bureau, West Bengal, 37/1/2, Belgachia Road, Kolkata, West Bengal - 700037. |
| New Delhi (CFPB) | National Apex Body under NCRB; manages NAFIS and coordinates with all states. | National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Ministry of Home Affairs, NH-8, Mahipalpur, New Delhi - 110037. |
| Mumbai | Serves India's financial capital; one of the busiest bureaus for criminal cases and PCCs. | Fingerprint Bureau, 2nd Floor, European Bungalow, Opp. Mata Ramabai Ambedkar Marg Police Station, Crawford Market, Mumbai – 400001. |
| Chennai | One of the oldest bureaus; processes a high volume of PCCs for residents traveling abroad. | State Crime Records Bureau (SCRB), Santhome High Road, Raja Annamalai Puram, Chennai, Tamil Nadu - 600028. |
| Bangalore | Located in India's Silicon Valley; focuses on integrating digital forensics with fingerprinting. | Fingerprint Bureau, SCRB, CID Annexe Building, Carlton House, Palace Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka - 560001. |
| Hyderabad | Serves a major tech hub; a center of excellence for forensic training. | Operates from the office of the Director General of Police (DGP), Lakdi-ka-pul, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500004. |
| Gandhinagar | Part of an advanced state forensic setup, integrating multiple forensic disciplines. | Directorate of Forensic Science, DFS Headquarters, Sector 18-A, Near Police Bhavan, Gandhinagar, Gujarat - 382018. |
| Lucknow | Manages one of the largest state databases for India's most populous state, Uttar Pradesh. | Finger Print Bureau, Police Bhawan, 7th floor, 4th Tower, near EKANA Stadium, Gomti Nagar Vistar, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh. |
Comments