
Introduction
Contactless payment card usage has considerably increased globally amid the covid 19 crisis. According to the results of a recent survey conducted by Mastercard, 79% of surveyed consumers worldwide are now using tap-and-go payments, while VISA says it is 48% of their customers. Contactless payments by analyst firm Juniper Research forecast that the value of global contactless transactions will treble from USD 2 trillion in 2020 to USD 6 trillion in 2024.
Insight of the increase in the contactless payment method during the pandemic crisis; various governments across the globe have increased the bars of the maximum single payment limit. Rising the limits allows customers to use contactless cards to purchase a wide range of products, including luxury items. However, higher limits might bring greater risk, particularly from loss and theft. However, there is a need to expand the limit and promote contactless payment options over time. Even though the use of contactless payment cards is skyrocketing, more than 50% of people are concerned about fraud if their contactless payment cards are lost. It is here that biometric cards come into play as the most secure contactless payment solution. Governments can use this to raise the bar for standard card withdrawal capacity. Prominent companies like MasterCard and Visa cards have already introduced such cards in limited markets.
The pandemic has fueled payment card companies to expedite biometric payment card allotment with the collaboration of biometric manufacturers. In fact, according to UBS analysts, biometric payment cards may account for 15% of the worldwide card industry within the next five years. Mastercard plans to wipe out magnetic strips from their payments within 2025; instead, they will use biometric contactless payment only. Biometric cards are, indeed, the future of contactless payment cards.
How biometric payment card works
The biometric payment card will have a fingerprint sensor powered by a microchip. The sensor will capture the fingerprint and compare it to the template already stored in the chip during the transaction. Only if the fingerprint matches the template will the transaction be performed. The card supports both biometric and pin transactions. Users that are unable to use fingerprints can use pin transactions.
Enrollment:
Enrollment is performed once per device at the bank in the presence of a bank official. This process is to create the fingerprint template inside the card.
Verification:
Step 1:Tap the card on the POS device, withholding the finger on the sensor.
Step 2:The sensor will match the digital image of the fingerprint against the stored template.
Step 3:The transaction is authorized if the fingerprint verification is successful. If the sensor does not identify the cardholder's fingerprint, the card will request the cardholder for a PIN or signature.
How the biometric payment card will work without a battery
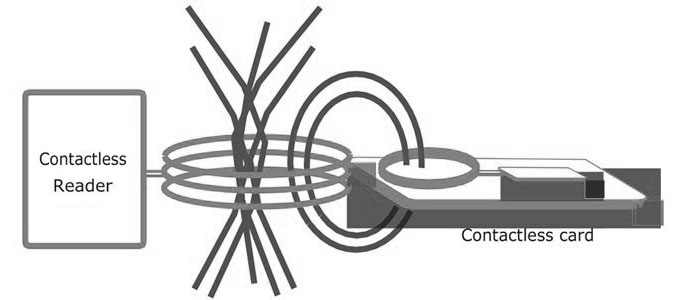
The biometric payment card is an electronic device that consists of a chip and fingerprint sensor. Obviously, the card needs a power supply to transmit data and scan fingerprints. The contactless card works under the ISO 14443 standard that governs wireless transactions. Using RFID technology, the POS device will power the payment card when it is within 4cm of the POS equipment's electromagnetic field.
Security of biometric data
The biometrics data on the payment card never leaves the card. The fingerprint does not need to be stored on any bank server; it is just needed to initiate the transaction in the card by authenticating the cardholder. At the same time, the card won't transfer fingerprint data. It is similar to biometric locks on smartphones and biologin devices.
Payment card for social benefits
Since the biometric payment card identifies the account holder, it may be used to identify the account holder in subsequent banking operations. For example, to deliver funds from government social welfare schemes. Card issuers can use this biometric identification technology to verify that such scheme benefits only the legitimate cardholder.
Bottomline
Traditional passwords and PINs are authentication methods, which means a third-party person can authenticate the card for the cardholder. Biometrics, unlike PINs and passwords, is a means of identification. That means the biometric payment card knows its owner. The only reason for the slow adoption of biometric cards is the high cost of manufacturing. However, eventually, leveraging biometric identification, contactless payment cards can takeover magnetic strip transactions.
Digvijay Dasondhi
Need for APi intrigetion
Reply